本文主要提供了 Django 字段、查询方面的优化建议,同时还介绍了一个 Django-silk 性能分析工具。希望对你开发高性能的 Django 工程有所帮助。
1. DBA 的建议
1.1 表字段设计
- 避免出现 null 值,null 值难以查询优化且占用额外的索引空间
- 尽量使用 INT 而非 BIGINT,尽可能准确描述字段
- 使用枚举或整数,替代字符串类型
- 使用 TIMESTAMP 替代 DATETIME
- 单表字段不要超过 20
- 使用整型存储 IP
1.2 索引
- 在 Where 和 Order By 操作上建立索引
- 值分布稀少的字段不适合建立索引
- 字符串最好不要作为主键
- 在应用层保证 UNIQUE 特性
1.3 SQL 查询
- 不要做列运算,可能导致表扫描
- 避免 %xxx 式查询
- 减少 JOIN 操作
- 使用 LIMIT 拿取分页数据,而不要拿全部
2. Django Model 建议
ORM 与 DB 的对应关系:
使用 db_index=True 添加索引
1
| title = models.CharField(max_length=255, db_index=True)
|
利用组合在一起的字段名字建立索引
1
2
| class Meta:
index_together = ['field_name_1', 'field_name_2']
|
组合在一起的字段名称唯一,可以是多个元组,也可以是单个元组。
1
2
3
| class Meta:
# 多元组
unique_together = (('field_name_1', 'field_name_2'),)
|
1
2
3
| class Meta:
# 单元组
unique_together = ('field_name_1', 'field_name_1')
|
3. 查询建议
select_related 通过多表 join 关联查询,一次性获取所有数据,减少查询次数。这样讲,可能还是不够明白,看看下面的例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| class Country(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
def __unicode__(self):
return self.name
class House(models.Model):
country = models.ForeignKey(Country, related_name='houses')
|
如果需要查询某个 country 的房屋信息,然后序列化处理。通常情况,可能会这样写:
1
2
3
4
5
| houses = House.objects.filter(country=country)
for item in houses:
# 会产生新的数据库查询操作
country_name = item.country.name
...
|
由于 Django 的 Lazy 特性,在执行 filter 操作时,并不会将 country 的 name 字段取出,而是在使用时,实时查询。这样会产生大量的数据库查询操作。
使用 select_related 可以避免这种情况,一次性将外键值取出。
1
2
3
4
5
| houses = House.objects.filter(country=country).select_related('country')
for item in houses:
# 不会产生新的数据库查询操作
country_name = item.country.name
...
|
prefetch_related 主要针对一对多、多对多关系进行优化。看一个例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| class Tag(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
class Article(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=32)
tags = models.ManyToManyField(
to="Tag",
through='Article2Tag',
through_fields=('article', 'tag'),
)
|
如果需要查询指定 Article 的 Tag 信息,然后序列化处理。通常情况,可能会这样写:
1
2
3
4
| articles = Article.objects.filter(id__in=(1,2))
for item in articles:
# 会产生新的数据库查询操作
item.tags.all()
|
同样,上面的查询会产生 N + 1 问题,导致大量 IO 消耗。如果使用 prefetch_related,可以避免在循环中持续进行数据库查询操作。
1
2
3
4
| articles = Article.objects.prefetch_related("tags").filter(id__in=(1,2))
for item in articles:
# 不会产生新的数据库查询操作
item.tags.all()
|
3.3 仅查询需要的数据
默认情况下, Django 查询时会提取 ORM 中的全部字段。但是在使用场景中,我们仅关注某些字段。为了节省查询多余字段的时间,可以使用 Django 提供的这两个函数:
1
| Entry.objects.defer('headline', 'body')
|
1
| Entry.objects.only("body", "rating").only("headline")
|
defer 和 only 的使用很灵活,可以链式延时加载,也可以链式逐步加载,还可以混合使用。
4. Django-silk 性能测试工具
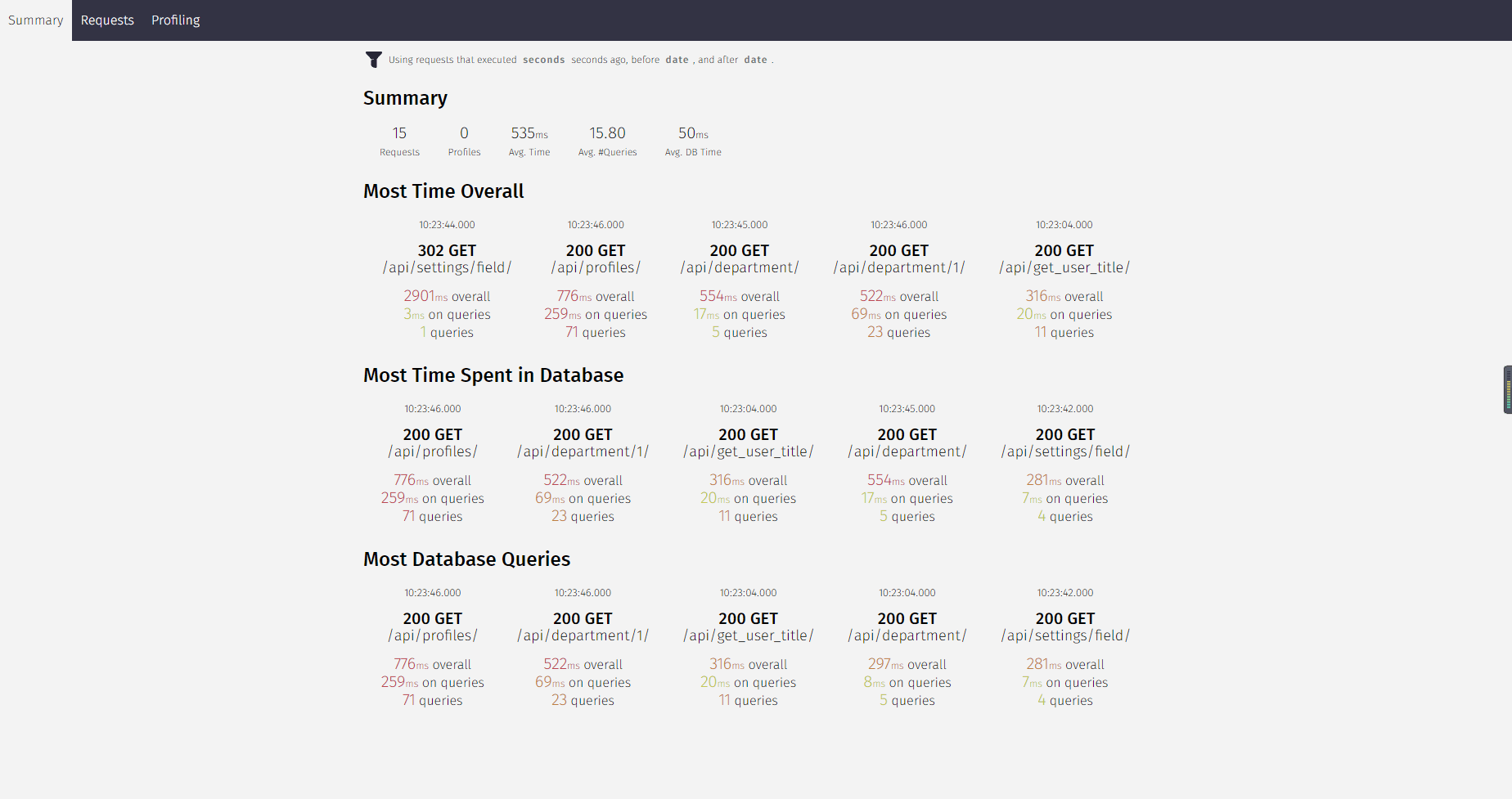
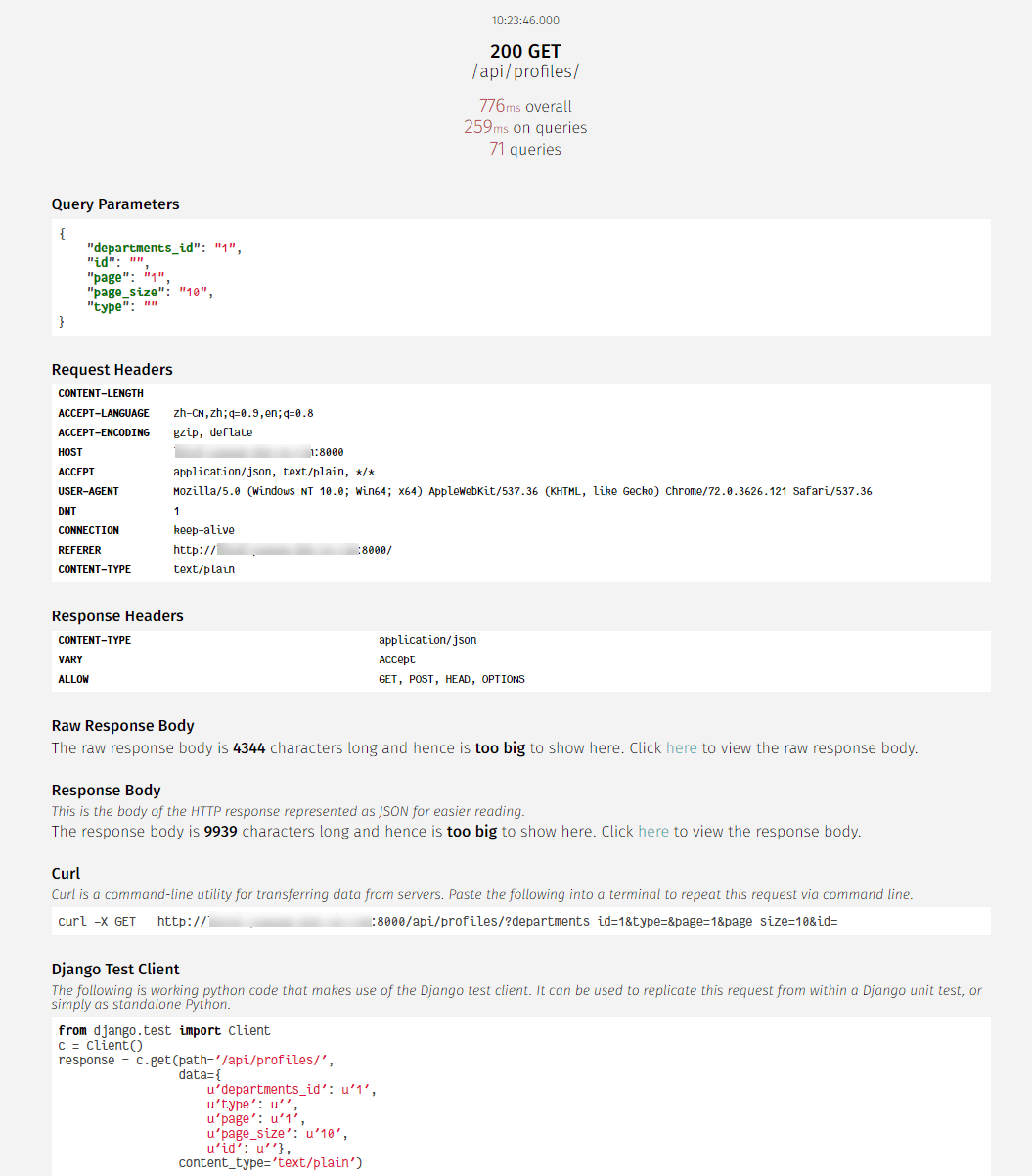
Django-silk 是一个 Django 的性能分析工具,提供 Django 的性能分析报告、API 的 SQL 语句、执行时间等。
1
| pip install django-silk==2.0.0
|
在 settings.py 中添加如下配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| MIDDLEWARE_CLASSES = (
...
'silk.middleware.SilkyMiddleware',
...
)
INSTALLED_APPS = (
...
'silk'
)
|
在 urls.py 中添加如下配置:
1
| urlpatterns += [url(r'^silk/', include('silk.urls', namespace='silk'))]
|
1
| python manage.py migrate
|
总览
API 详情
5. 参考


